Sepsis (septicemia, blood poisoning)
Septicemia (blood poisoning) - an acute or chronic disease characterized by progressive proliferation in the organism of bacterial, viral and fungal flora. Sepsis can result from bacterial infection of the body of a famous chamber inflammation (abscesses), but often enough atrium remains unclear. Sepsis can occur acutely, sometimes almost at lightning speed (when in the absence of proper treatment, death occurs within hours or days) or chronically. Currently, the nature of the course of sepsis is largely unchanged as a result of early antibiotic therapy.
Etiology.
Agents of sepsis can be pathogenic, opportunistic microorganisms: cocci (staphylococci, pneumococci, meningococci), E. coli, B-negnoynaya coli, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Klebsiella and others; viruses herpetiformis group and others, fungi such as Candida, Aspergillus.
Pathogenesis.
Generalization of infection by the pathogen prevalence over the bacteriostatic capacity of the organism as a result of a massive invasion (eg, ulcer breakthrough in the blood of an infected blood clot, while trying to squeeze a boil, infected trombotsitnoy of the masses, etc.), either congenital or acquired reduction of immunity. Immunity disorders prior to sepsis, as a rule, remain indefinable, except depression of hematopoiesis. However, sepsis does not occur as a result of immunity disorders in general, and as a result of failure in any one of its units, leading to a breach of antibody production, decreased phagocytic activity or the activity of lymphocyte production, etc. Therefore, in most cases of sepsis caused by a pathogen, breeding which normally prevents the immune response, ie, defined by its link, which proved genetically damaged or acquired, change agents within a disease is the exception rather than the rule. Simultaneous coexistence of multiple agents, they change observed in the immunosuppression induced by the use of cytotoxic drugs, depression, blood as a result of aplasia of the bone marrow or leukemic lesions, an intense insolation and sunburn, rough suppress the immune response in a few links. Recurrent septic bacterial infection marked by an inherited defect of complement C2, properdin, and other factors of the complement system. For gross defects of immunity is often a so-called opportunistic infections caused by conditionally pathogenic flora saprophytes. Approximately 10% of septic conditions due to a combination of pathogens. Polymicrobial sepsis occurs in disorders of immunity, associated with the absence of spleen, violations of the cellular (T-helper) immunity in AIDS.
In adults and children without obvious causes immunodeficiency (cytostatic, steroid therapy, etc.) are most likely causative agent of sepsis is Staphylococcus or Streptococcus pneumoniae, rarely meningococcus. On the background of cytostatic therapy (especially in nosocomial infection), plays an important role Gram microflora (gut or blue pus Daddy, Proteus). The causative agent of sepsis from an infected aortic aneurysm thrombus, the inferior vena cava (distapnee installed it a filter), the subclavian vein (at long distance it catheter) may be staphylococci, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Limfopropiferativnye limfofanulematoz tumor and are accompanied by violation of antiviral immunity, leading to generalized herpetic infections (chickenpox, shingles, herpes simplex) until sepsis. When violations neytrofilopoeza a result of hereditary neutropenia meet recurrent staphylococcal infections sometimes with the development of staphylococcal sepsis. Chronic administration of steroid hormones may be chronic or acute bacterial septic processes and tuberculous sepsis.
After removal of the spleen (for any reason) there is a predisposition to septic conditions often meningo-coccal or pneumococcal. The spleen is capable englobe neopsonizirovannye not associated with antibodies bacteria, encapsulated bacteria (eg, pneumococci and meningococci), while in liver only good phagocytized opsonized bacteria. In order that the liver has the function of the destruction of encapsulated, neopsonizirovannyh bacteria after removal of the spleen, it is necessary to introduce large amounts of fresh plasma containing opsonins. After splenectomy plasma levels of opsonins, as properdine, tuftsin produced mainly spleen and necessary for the phagocytosis of microorganisms by neutrophils is reduced. Properdin is also a factor that triggers additional path activation of the complement system (a component of the PFAs) - one of the most important parts of humoral immunity. Finally, the spleen is produced mainly immunoglobulin M. Lack of all these factors contribute to the development of deadly postsilenektomicheskogo syndrome.
Important role in the spread of infection is the formation of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Massive infection is the basis of tissue decay, release into the blood kinins and proteolytic enzymes that contribute to a violation of vascular permeability, stasis, thrombosis in the microcirculation system. Multiple thromboses become a medium for the growth of microorganisms. In the development of DIC in sepsis play a significant role endotoxin - lipopolysaccharide from the walls E. coli capsular polysaccharide of pneumococcus, coagulase produced by Staphylococcus aureus capsule, and other products of the bacterial cell. One of the most studied ways of excitation of DIC in sepsis - activation of coagulation factor XII (Hageman factor). Affecting sosudistuto wall, endotoxin activates factor XII, leading to increased clotting, the formation of kallikrein and its predecessors, and with them, to the activation of fibrinolysis (plasminogen conversion to plasmin-on), the formation of kinins, activation of the complement system. Accumulation of bradykinin leads to the development of shock-falling blood pressure, increase vascular permeability and microcirculatory disorders.
DIC and shock-standing complications of sepsis caused by gram-negative organisms, meningokokkamii, the acute pneumococcal and staphylococcal sepsis. Accumulation of kinins in sepsis and DIC contributes to depletion of enzymes such as kininaza, an inhibitor of kallikrein, is usually contained in the plasma of healthy individuals. Activated at the beginning of DIC fibrinolysis and then sharply decreases due to depletion of Hageman factor, kallikrein, plasminogen itself. Inhibition of fibrinolysis is a characteristic sign of DIC complicating sepsis. When infection microthrombi DIC inevitably leads to severe multiorgan pathology in the pathogenesis of which is crucial in the beginning itself the infection, and after 2-3 weeks-pathology of immune complexes. Clear distinction between proper septic organ pathology and by immune syndromes after the elimination of the main bacterial and mikrotromboticheskogo processes do not exist. Inactivated, but nefagirovannye bacteria in the blood clot may remain active and cause recurrent disease, to facilitate its transition into a chronic, often monoorganny process. DIC is almost obligatory in the pathogenesis of sepsis, the disappearance of his laboratory and clinical signs indicative of successful treatment.
Thrombocytopenia and reduction of clotting may be due not only to the consumption of platelets and clotting factors in the thrombus. In connection with the infection, antibodies, immune complexes activated by phagocytosis (in particular, phagocytosis of neutrophils), with the enzymes released from neutrophil elastase, hemotripoin. The excess of proteolytic enzymes contribute to tissue damage (in particular, the vascular wall), lysis of platelets and clotting factors are not, which leads, in turn, to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome and acute respiratory distresssindroma.
The clinical picture of sepsis depends on the causative agent, the source of infection and immune status. Onset may be rapid with a spectacular chills, pyrexia, myalgia, a hemorrhagic or papular rash or gradually with a slowly growing intoxication and a gradual increase in body temperature. By frequent, but nonspecific signs of sepsis include enlargement of the spleen and liver, expressed sweating after fever, severe weakness, physical inactivity, anorexia, constipation. In the absence of sepsis, antibiotic therapy, usually results in death from multiple violations of all organs and systems. Characterized by thrombosis (particularly lower limb veins) in combination with hemorrhagic syndrome.
With adequate antibiotic therapy against lowering the temperature, reduce toxicity in 2-4 weeks from the onset of the disease appear arthralgia (up to the development of arthritis), symptoms glomeruponefrita (protein, red blood cells, the cylinders in the urine), the symptoms poliserozita (pleural friction rub, pericardial friction sound ) and myocarditis (tachycardia, gallop rhythm, transient systolic murmur at the apex or pulmonary artery, expansion of the boundaries of the relative dullness of the heart, reducing or even negativizatsiya T wave and ST segment shift down mainly in the anterior chest leads). This symptoms arising on the background to improve key indicators of septic
process and related to the pathology of immune complexes should not be confused with signs of septic actually, a bacterial disease. The main manifestations of the latter occur in the early days of the disease and are characterized by all the signs of septic process in a particular organ (suppurative myocarditis, endocarditis, the variants of septic lung and kidney). Crucial role in the treatment of sepsis are massive antibiotic therapy and anti-DIC (see Chapter 7).
In severe DIC, respiratory distress syn-drome observed multiple discoid atelectasis and unstable polymorphic shadows in the lungs caused by interstitial edema. Similar changes are observed in severe sepsis regardless of causative agent and the X-ray unit is almost indistinguishable from pneumonia. However, for the shadows of the inflammatory nature characterized by resistance, and for the shadows interetitsialnogo edema - evanescence. Auscultation of lung interstitial edema may indicate nezvuchnye finely wheezing, crepitation.
Diagnosis.
Start any heavy inflammatory process, accompanied by chills, high body temperature, at first glance, difficult to distinguish from early sepsis. However, the rapid temperature rise to 39-40 (C, stunning chills, general grave condition without the expressed monoorgannoy Pathology, high leukocytosis with a shift of band of 20-30%, clinical and laboratory signs of DIC were sufficient grounds for the diagnosis of sepsis and implementation of appropriate intensive therapy. The diagnosis of sepsis is essential to bind to a particular pathogen, as bacteriostatic, antiviral and antifungal therapy is strongly specific. Establishing an etiologic diagnosis is very difficult and not always possible. Blood cultures, identification of specific bacterial antigens in the 50-60% of the cases do not give answer to the question about the nature of the pathogen in the first days of illness, determine when a particular treatment strategy. Diagnosis of sepsis in identifying the nature of the pathogen requires daily blood cultures regardless of the negative responses in the first days of illness and the ongoing antibiotic therapy, makes the possibility of positive culture less and less likely . an important role in establishing the causative agent of sepsis are clinical features of disease and its first symptoms.
Staphylococcal sepsis is characterized by spectacular chills, high fever, the appearance of pain in muscles and bones. Muscle pain can be almost €morfiynoy€ intensity. Usually at this skin you can see individual papules negemorragicheskoy nature sometimes with the formation of tiny bubbles on top of pimples. General state of patients with severe, but the total depth of oppression no clear consciousness, the patients clearly talk about their feelings. The X-ray revealed multiple pulmonary often almost the same size and density of the cloud-shadows, which are then merged, forming irregular foci and areas of decay. At the beginning of the process noted a dry cough, then it becomes wet with abundant discharge of yellowish sputum. The resulting lung abscess may break in the pleura with the development of empyema. Myalgia are often the result of microabscesses in the muscles. Further, the formation of multiple phlegmon, osteomyelitis lesions, abscesses of the liver, kidneys and other organs.
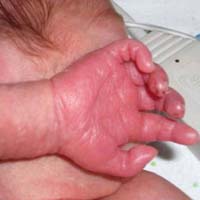
Meningococcal sepsis is different often stormy start with very severe intoxication, enteropathy, which in a few hours can lead to shock, characterized by progressive congestion, rapidly upcoming loss of consciousness. A number of patients on the skin appear abundant polymorphic or monomorphic papular hemorrhagic rash. The observation that the rash becomes the basis for the assumption of meningococcus-hand nature of sepsis and the immediate destination of large doses of penicillin intravenously. Hemorrhagic lesions showed severe DIC, they capture not only the skin but also subcutaneous tissue, and therefore evolving on their site necrosis may be deep enough. Heavy mikrotrombotichesky process facilitates the rapid formation of deep ulcers, it lies at the basis of the clinical picture of glomerulonephritis (up to the development of anuria) and hepatitis (mild elevation of bilirubin, gipertransaminazemiya, with increased liver). Severe complication of meningococcal sepsis, hemorrhage in both adrenal glands (due to DIC) that makes the clinical picture of shock. On the background of improving the patient's condition and the normalization of temperature meningococcal septicemia may be complicated by the symmetrical gangrene (dry or wet) your toes, but with little active treatment DIC - and more extensive gangrene, requiring amputation. In the hemogram is often determined by hyperskeocytosis stab shift to 20-40%. Clinical improvement and the dynamics of the blood picture may not match: leukocytosis and stab shift sometimes remain on the background of a normal body temperature, which is under the influence of a powerful antibiotic drops for a few days, and multiple organ pathology and deep necrosis remain for several weeks. Along with high leukocytosis and thrombocytosis occurs (sometimes up to 1 million or more platelets in 1 ml of blood), particularly due to activation of hematopoietic colony-stimulating factor under the influence of interleukin-I, produced by macrophages, antigen processing agent.
As the level of interleukin-I (as an endogenous pyrogen) associated fever, neutrophilia, proliferation of T-helper cells, antibody.
Pneumococcal sepsis is characterized by the usual start of sepsis: a terrific fever, elevation of body temperature to 39-40 "C. However, in these cases there is a severe intoxication with weakness, but without loss of consciousness and shock. Patients respond to questions in monosyllables, is dwindling fast. Eruptions on the skin , myalgia, cellulitis and other manifestations of pneumococcal sepsis septikoliemii not peculiar. revealing the absence of severe organ pathology on the background of a very serious general condition. The distinctive feature of the disease is often preserve a small percentage of eosinophils in the blood, whereas other types of bacterial sepsis characterized aneozinofiliya. Leukocytosis with pneumococcal sepsis moderate, but stab shift can be expressed. Hemorrhagic syndrome is usually absent. Current pneumococcal sepsis is not as rapid as meningococcal (exceptions may be!), but the improvement under the influence of antibiotic therapy also does not occur as rapidly as in meningococcal sepsis.
The first signs of the adequacy of treatment are reduction of weakness, loss of shivering, the emergence of appetite, although the body temperature even for a few days can be increased, only revealing a downward trend. Underestimation of the subjective indicator of improvement is very dangerous, because the absence of laboratory signs of improvement against the background of persistent febrile temperatures could create a wrong impression about the inefficiency of antibiotic therapy, while it is penicillin (and not the broad-spectrum antibiotics) is shown in pneumococcal sepsis throughout the disease, continued for many weeks and sometimes months (for example, when an infected thrombus in large vessels). On the premature withdrawal of penicillin showed a relapse of fever, worsening of general condition, the resumption of chill. All of this requires no change of the antibiotic, and return to treatment with penicillin in large doses (usually with pneumococcal and meningococcal sepsis dose of penicillin for adults is 20 000 000-24 000 000 IU / day should not significantly increase, since at doses 30,000 000-40 000 000 IU / day may develop severe hemolysis, pantsitoliz or hemorrhagic syndrome caused disaggregation of platelets). Feature of pneumococcal sepsis is a low intensity or complete absence of bright organ manifestations of the disease, although this type of sepsis, like others, may be complicated by immune syndrome or that character.
Sepsis caused by gram-negative organisms (Escherichia coli, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) occurs either in the presence of large entrance gate (postoperative abdominal abscesses, abscesses in the pelvis after gynecologic procedures, infected thrombus in the aneurysmal aorta extended), or the sudden suppression of immunity (cytostatic therapy, lymphoproliferative tumors of the blood, acute leukemia). In the diagnosis of these forms of sepsis is crucial bacteriological analysis - blood cultures, urine, sputum, bacterioscopy secretions from wounds and prints wound surfaces. One manifestation of Pseudomonas sepsis (sometimes staphylococcal) becomes necrotic hemorrhage: rash (occasionally single) Saturated dark red, almost black, surrounded by dark red wall and erect above the skin surface. These sometimes painful (especially at the beginning) of education is gradually rising, the body temperature remains febrile, having child screenings in other parts of the skin and internal organs (found at postmortem examination). Necrotic hemorrhage almost defy conventional types of antibiotic therapy because of surrounding dense thrombotic shaft, but within these structures there is an active pathogenic flora. Mechanism for the formation of necrotic hemorrhage, apparently close pathogenesis noma and gangrene, in which the decisive role played by necrosis, surrounded by a gradually expanding zone of thrombosis: infection triggers blood clots, blood clots are breeding grounds for microbial growth and block the flow of antibiotics in the necrotic center. The process is self-sustaining due to exhaustion of fibrinolysis. The primary means of breaking this vicious circle is the topical application of dimethyl sulfoxide with an antibiotic against conventional therapy and improve fibrinoliticheskoi activity of blood through the massive transfusion of fresh frozen plasma.
Sepsis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, against the background of immunosuppression (for cytostatic therapy, tumors of blood) at different weight and rapidly developing shock. Same sepsis originating from the normal parameters of blood as a result of breakthrough infection from an infected blood clot can occur torpidly; the condition of patients worsens gradually, antibiotic therapy has a positive effect bo unstable. General sepsis caused by gram-negative microflora, without the entrance gate, under normal composition of leukocytes and without the use of immunosuppressive drugs is very unlikely. For sepsis, is quick development of shock (sometimes literally within 2-3 hours of the onset of febrile temperature).
Diagnosis of sepsis caused by gram-negative microflora in hematology and oncology hospitals are often borne by the doctor on duty, who, nevertheless, before the start of antibiotic therapy (along with the first antibiotics) should take blood for culture in any sterilely and put the dishes in an incubator at 37 "C. In the diagnosis of sepsis should not neglect any symptom to assess the nature of pathogens. So, if the source of sepsis was some kind of festering cavity (empyema, abscess mezhkishechny, etc.), the nature of the microflora are trying to determine to some extent by smell.
Clinical sign of a change agent on the background of the current septic process is the change in clinical disease: against the background of the progressive improvement of the sudden temperature rises Tepa, there is fever, leukocytosis and increases again reveals a pronounced shift of band. Such changes are possible due to the formation septikopiemicheskoy cavity. Therefore, while searching for a new agent should be all means exclude the presence of an abscess of the internal organs (intrahepatic abscess, carbuncle and the kidneys, etc.).
Sepsis caused by herpes viruses, is found almost exclusively on the background of severe immunosuppression with lymphoproliferative diseases (including acute lymph-foblastny T-kpetochny leukemia), chlamydia. Diagnosis of generalization zoster virus is not difficult when the process begins with a short characteristic of segmental lesions. Then a rash spreading all over the skin and occur on the oral mucosa, trachea, bronchus, esophagus, vocal cords. Likewise, may leak and sepsis caused by varicella-zoster virus, at least - the herpes simplex virus. In the expanded picture of all three processes are virtually indistinguishable. Damage to the surface lesions, removal of crusts (do not!) May be accompanied by a secondary infected elements of an eruption and development are usually staphylococcal sepsis.
Treatment of sepsis
should be primarily pathogenic. As a crucial role in the development of sepsis (unlike any other infection) play the massiveness of infection, the presence of microorganisms in the blood and all tissues combined with severe disseminated intravascular coagulation, then the therapy is directed against two components of the process - the infection and DIC . Septic patients should be hospitalized immediately suspected him in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. Hemorrhage in the adrenal gland, limb gangrene, irreversible changes in the internal organs are a consequence of late pathogenetic therapy of septic patients.
Following the diagnosis of venous blood taken for culture for biochemical studies (bilirubin, prothrombin, transaminases, LDH, creatinine, protein fraction) and for analysis of blood coagulation (fibrinolytic activity, protaminsulfatny and ethanol tests, fibrinogen degradation products). In the study of blood platelet count is required, and then reticulocytes. Immediately after blood collection on various studies by the same needle into a vein antibiotic, respectively, the nature of the alleged infection, but in the largest possible doses. If there are pronounced signs DIC (in particular, abundant rash, especially hemorrhagic in nature), myalgia and muscle tenderness to palpation, polymorphic shadows of interstitial pulmonary edema, or more or less the same type of Shadows hematogenous dissemination of infection in the radiograph of the chest cavity must be immediately initiated plasmapheresis . Removed about 1.5 liters of plasma, replacing it with about 2 / 3 of an appropriate amount of fresh frozen plasma. In severe sepsis, the amount of transfused fresh frozen plasma may exceed the volume of removed plasma to enter at the same time must be at least 2 liters of fresh frozen plasma.
Apart from the above symptoms DIC, should be considered a symptom of thrombosis during venipuncture needle, and a quick thrombosing after Prokop finger for a blood test. On the background of sepsis, these signs is sufficient for reliable diagnosis of DIC. Following plasmapheresis, and if necessary, during its holding applied heparin at 20 000-24 000 IU / day for adults. Heparin was injected iv infusion either continuously or hourly. Increase the intervals between doses of heparin, at least in the first day of treatment, you should not. The presence of hemorrhagic syndrome - not a contraindication, and an indication for treatment with heparin. If plasmapheresis is not feasible, it is necessary the introduction of fresh frozen plasma to the same extent as in plasmapheresis. In the early days of treatment undesirable subcutaneous and intramuscular injections.
If hypotension is used simpatomimeti-ki, with a steady decline in blood pressure intra-tively administered hydrocortisone or prednisolone at a dose sufficient to stabilize the patient's condition, after which steroid hormones override the same day, and after prolonged use (if there is no bleeding in the adrenal glands , the duration of glucocorticoid therapy is extremely undesirable) - within 2-3 days. By itself, hypotension is not a contraindication to plasmapheresis, which follows in this case begins with an introduction to / from 500-1000 ml of fresh frozen plasma and perform in a small volume (500-800 ml of plasma removed).
For long-term and multiple intravenous infusions usually there is a need in the catheterization of one of the peripheral and less central veins. It should be remembered here that the delayed rises in body temperature (after several days of steady decline) may be a consequence of vein thrombosis around the catheter, and infection with a blood clot or adjacent subcutaneous tissue, the skin at this point is hyperemic. In such cases, the catheter or remove all, or injected into another vein.
Antibacterial therapy of sepsis is determined by the type of alleged or established by the pathogen. If no clinical or laboratory signs do not allow any certainty to establish an etiological factor, then prescribe a course of so-called empirical antibiotic: gentamicin (160-240 mg / day) in combination with tsefaloridinom (tseporinom) or cefazolin (kefzolom) at a dose 4 g / d / in. Evaluate the effectiveness of antibacterial therapy on Fox the other therapeutic measures necessary to improve the subjective condition of the patient, stabilize blood pressure, reduced body temperature, disappearance of fever, decrease in the number of old or absence of new lesions on the skin. By the laboratory grounds effectiveness of antibiotics include reduction in the percentage of band elements in the formula of blood. Clear weighting of the state of all these indicators in the next 24-48 hours, and deterioration of health of patients on the following day after the start of antibiotic treatment proves ineffective selected antibiotics and the need to replace them.
The following scheme of empirical antibiotic therapy suggests that sepsis is not due to staphylococcus, nezyvaemogo Escherichia coli, characterized by the absence of organ pathology and pyosepticemia, the rapid development of shock (sometimes literally within 2-3 hours of the onset of febrile temperature).
Diagnosis of sepsis caused by gram-negative microflora in hematology and oncology hospitals are often borne by the doctor on duty, who, nevertheless, before the start of antibiotic therapy (along with the first antibiotics) should take blood for culture in any sterilely and put the dishes in an incubator at 37 "C. In the diagnosis of sepsis should not neglect any symptom to assess the nature of pathogens. So, if the source of sepsis was some kind of festering cavity (empyema, abscess mezhkishechny, etc.), the nature of the microflora are trying to determine to some extent by smell.
Clinical sign of a change agent on the background of the current septic process is the change in clinical disease: against the background of the progressive improvement of the sudden temperature rises Tepa, there is fever, leukocytosis and increases again reveals a pronounced shift of band. Such changes are possible due to the formation septikopiemicheskoy cavity. Therefore, while searching for a new agent should be all means exclude the presence of an abscess of the internal organs (intrahepatic abscess, carbuncle and the kidneys, etc.).
Sepsis caused by herpes viruses, is found almost exclusively on the background of severe immunosuppression with lymphoproliferative diseases (including acute lymphoblastic leukemia T-kpetochny), chlamydia. Diagnosis of generalization zoster virus is not difficult when the process begins with a short characteristic of segmental lesions. Then a rash spreading all over the skin and occur on the oral mucosa, trachea, bronchus, esophagus, vocal cords. Likewise, may leak and sepsis caused by varicella-zoster virus, at least - the herpes simplex virus. In the expanded picture of all three processes are virtually indistinguishable. Damage to the surface lesions, removal of crusts (do not!) May be accompanied by a secondary infected elements of an eruption and development are usually staphylococcal sepsis.
Treatment of sepsis should be primarily pathogenic. As a crucial role in the development of sepsis (unlike any other infection) play the massiveness of infection, the presence of microorganisms in the blood and all tissues combined with severe disseminated intravascular coagulation, then the therapy is directed against two components of the process - the infection and DIC . Septic patients should be hospitalized immediately suspected him in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. Hemorrhage in the adrenal gland, limb gangrene, irreversible changes in the internal organs are a consequence of late pathogenetic therapy of septic patients.
Following the diagnosis of venous blood taken for culture for biochemical studies (bilirubin, pro-thrombin, transaminases, LDH, creatinine, protein fraction) and for analysis of blood coagulation (fibrinolytic activity, protaminsulfatny and ethanol tests, fibrinogen degradation products). In the study of blood platelet count is required, and then reticulocytes. Immediately after blood collection on various studies by the same needle into a vein antibiotic, respectively, the nature of the alleged infection, but in the largest possible doses. If there are pronounced signs DIC (in particular, abundant rash, especially hemorrhagic in nature), myalgia and muscle tenderness to palpation, polymorphic shadows of interstitial pulmonary edema, or more or less the same type of Shadows hematogenous dissemination of infection in the radiograph of the chest cavity must be immediately initiated plasmapheresis . Removed about 1.5 liters of plasma, replacing it with about 2 / 3 of an appropriate amount of fresh frozen plasma. In severe sepsis, the amount of transfused fresh frozen plasma may exceed the volume of removed plasma to enter at the same time must be at least 2 liters of fresh frozen plasma.
Apart from the above symptoms DIC, should be considered a symptom of thrombosis during venipuncture needle, and a quick thrombosing after Prokop finger for a blood test. On the background of sepsis, these signs is sufficient for reliable diagnosis of DIC. Following plasmapheresis, and if necessary, during its holding applied heparin at 20 000-24 000 IU / day for adults. Heparin was injected iv infusion either continuously or hourly. Increase the intervals between doses of heparin, at least in the first day of treatment, you should not. The presence of hemorrhagic syndrome - not a contraindication, and an indication for treatment with heparin. If plasmapheresis is not feasible, it is necessary the introduction of fresh frozen plasma to the same extent as in plasmapheresis. In the early days of treatment undesirable subcutaneous and intramuscular injections.
If hypotension is used simpatomimeti-ki, with a steady decline in blood pressure intra-tively administered hydrocortisone or prednisolone at a dose sufficient to stabilize the patient's condition, after which steroid hormones override the same day, and after prolonged use (if there is no bleeding in the adrenal glands , the duration of glucocorticoid therapy is extremely undesirable) - within 2-3 days. By itself, hypotension is not a contraindication to plasmapheresis, which follows in this case begins with an introduction to / from 500-1000 ml of fresh frozen plasma and perform in a small volume (500-800 ml of plasma removed).
For long-term and multiple intravenous infusions usually there is a need in the catheterization of one of the peripheral and less central veins. It should be remembered here that the delayed rises in body temperature (after several days of steady decline) may be a consequence of vein thrombosis around the catheter, and infection with a blood clot or adjacent subcutaneous tissue, the skin at this point is hyperemic. In such cases, the catheter or remove all, or injected into another vein.
Antibacterial therapy of sepsis is determined by the type of alleged or established by the pathogen. If no clinical or laboratory signs do not allow any certainty to establish an etiological factor, then prescribe a course of so-called empirical antibiotic: gentamicin (160-240 mg / day) in combination with tsefaloridinom (tseporinom) or cefazolin (Kef-zolom) a dose of 4 g / d / in. Evaluate the effectiveness of antibacterial therapy on Fox the other therapeutic measures necessary to improve the subjective condition of the patient, stabilize blood pressure, reduced body temperature, disappearance of fever, decrease in the number of old or absence of new lesions on the skin. By the laboratory grounds effectiveness of antibiotics include reduction in the percentage of band elements in the formula of blood. Clear weighting of the state of all these indicators in the next 24-48 hours, and deterioration of health of patients on the following day after the start of antibiotic treatment proves ineffective selected antibiotics and the need to replace them.
The following scheme of empirical antibiotic therapy suggests that sepsis is not due to staphylococcus, no E. coli or meningococcus (meningococcal septicemia after failure of antibiotic treatment is usually manifested haemorrhagic rash). The smallest lesion of the internal organs is usually celebrated with pneumococcal sepsis. In this connection it is expedient to replace the cephalosporins on large doses of penicillin (20 000 000-24 000 000 IU / day / to over 8 injections or IV continuous infusion), while continuing therapy gen-tamitsinom.
If the results of this study suggest that sepsis caused by gram-negative organisms, patients designate carbenicillin (20-30 g / d / drip or bolus injections, 6-8), still continuing the use of gentamicin. Since carbenicillin is to disaggregate drugs (ie, prevents platelet aggregation), there are manifestations of non-severe hemorrhagic syndrome - more than usually marked hemorrhage at the injection, mechanical injury. If these antibiotics are effective, by itself hemorrhagic cider can not be seen as testimony to their abolition; only need a strict exception to the treatment of other disaggregated funds (primarily nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Treatment of established or suspected pneumococcal or meningococcal septicemia include in intravenous penicillin in the above doses. In virtually all cases of inefficiency penicillin therapy in these patients, it is a properly staged etiology. In assessing the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy of these two types of sepsis is important to pay attention to the subjective feeling better) to stabilize the process, the lack of deterioration over several days, not only in body temperature. All these features favor the efficacy of the therapy, are sufficient to maintain the treatment the same, without any fuss or undue change of antibiotics. Since the occurrence of penicillin-resistant strains among the pneumococci and meningococci is practically not observed, there is no reason to cancel this antibiotic during the entire course of treatment (at least 3 weeks), provided their performance.
Particularly difficult antibiotic therapy of sepsis occurred on the background of previous immunosuppression. In these cases, antibiotics or sulfonamides often have a temporary effect - the body temperature drops, being improved (in these cases, organ manifestations of sepsis are often not significant), but then suddenly starts again fever, chills, etc. In the history of such patients is often a wide range of applied antibiotics, providing a temporary positive effect. In these cases shows a therapy with gamma globulin, intravenous (including endobulin a dose of 1-2 g per 10 kg 1 every 7-10 days, but in severe sepsis, 2 times a week; endobulin nezhelatelnoispolzovat before plasmapheresis and in those days, when carried out transfusion of plasma, red cells, albumin and other protein drugs).
When staphylococcal sepsis therapy should begin with the application of an antibiotic from the group of cephalosporins, new, together with gentamicin (see above). If the effect is insufficient, gentamicin may be replaced by amikacin (500 mg 2-3 times a day) or tobramycin (80 mg 2-3 times a day). Even with the slight renal insufficiency cephalosporins may be sharply nephrotoxic (they are the kidneys). Nephrotoxicity and used in this scheme aminglikozidy (gentamicin, etc.). Therefore, these antibiotic therapy should be accompanied by a constant (2 times per week) controlled by the level of creatinine in blood, urine analysis and determination of urine output.
Worsening renal function requiring a cancellation of a number of antibiotics, or reduce their dose, are calculated by creatinine clearance, manifested a decrease in urine output (up to anuria, when you need an immediate massive plasmapheresis) and increase in serum creatinine beyond the upper limit of normal. Duration of antibiotic therapy in sepsis determined the existence of the main manifestations of the disease (including immunocomplex) is usually negative blood culture does not matter as a criterion for withdrawal of antibiotics.
Antibiotic therapy should continue at least 2-3 weeks at the most favorable prognosis. With the protracted process, signs of septic endocarditis, septikopiemicheskih foci of osteomyelitis antibiotic therapy continue for many months.
Thus, long-term directed antibiotic therapy, heparin, fresh frozen plasma, plasmapheresis, the main ways to treat sepsis, aimed at the destruction of the pathogen, activation of phagocytosis in the spleen and the factors of humoral immunity, opsonization of bacteria, suppression of kinins, the introduction of antiplatelet factor plasma plasminogen required for activation fibrinolysis. Plasmapheresis enhances excretion of damaged cells, bacteria, activates the phagocytic function of the spleen, which in sepsis, as a rule, is blocked.

Cheap Wedding Dresses, Beautiful Lace Bridal Gowns Online Seek fashion & cheap bridal/wedding gowns from thousands of quality wedding dresses online. Various affordable wedding dresses/gowns with big discount! toddler flower girl dresses