Giardiasis in children
Kramarev S.A.doktor Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Pediatric Infectious Diseases of the National Medical University. AA Bogomoltsa, chief pediatric infectious disease MoH Ukraine
Giardiasis - a widespread protozoan disease, for which may vary from subclinical to severe.
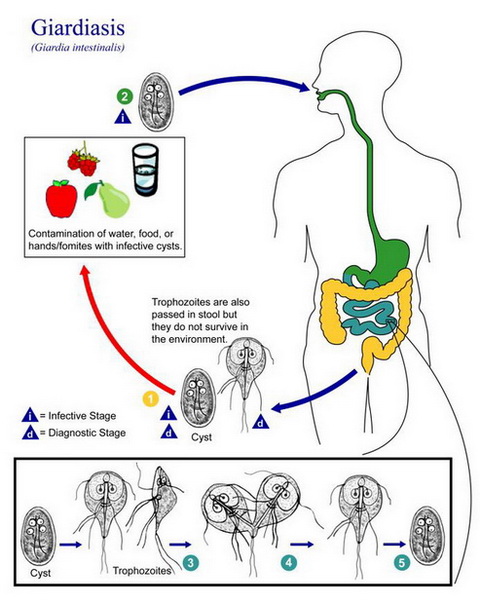
The causative agent of giardiasis is Lamblia intestinalis (Lamblia Giardia). In the human and animal Giardia exists in two forms. In a vegetative form, they are mainly the upper parts of the small intestine, and if it enters the colon turn into cysts (spore form), which are allocated with the faeces into the environment. In humid conditions, in the shadows, cysts retain their ability to live to 70 days in the soil - to 9-12 days, and the shortage of water - 4-5 days. The main source of infection is the man. However revealed that Giardia parasites in the body of cats, dogs and rodents. Of a sick child in the day with feces allocated to 900 million cysts pathogen, while infecting dose sostavlyaetvsego 10-100 cyst.
There are three main ways of transmission of giardiasis: water, contact-household and food industry. Dominates the waterway. Infection occurs most often in the use of poorly purified tap water or water from open reservoirs. In case of contact-domestic route of infection via zagryaznennyetsistami household items: clothes, toys, utensils, etc. Children who have unhealthy habits such as sucking fingers, pencils, pens, nail biting, virtually 100% of the cases detected Giardia. Possible contamination with cysts used infected food.
Proceeding through the mouth, cysts bypass bar er stomach (they are acid-shell) and enter the duodenum, where one of the cysts formed two vegetativnyeformy. Giardia attached to the villi of the mucous membrane of the proximal small intestine. Here they are adsorbed degradation products of food. Parasite Giardia in the small intestine accompanied by a number of pathological effects:
introduction in the lining of the small intestine causes the development of inflammation in it, that is the result of the cytopathic effects of metabolic products of the parasite;
as a result of inflammation of the intestinal mucosa appear subatrofic and atrophic changes resulting in damage to the brush border and the development of malabsorption, secondary fermentopathy;
violation of the binding of bile acids is the cause of skin itch, intestinal motility disorders, biliary dyskinesia;
reducing the synthesis of secretory immunoglobulin A leads to chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract;
as a result of long-term persistence of Giardia, the impact of their metabolites in the body is formed by a chronic syndrome of endogenous intoxication, secondary immune deficiency, sensitization.
Most of the patients with giardiasis occurs in a subclinical form. With a massive invasion of the clinical course with severe clinical symptoms and has acute or hronicheskoetechenie.
Acute giardiasis is more common in infants and is characterized by diarrhea syndrome in a typical acute intestinal infection, mainly affecting the small kishki.Obezvozhivanie lyamblioznoy for acute infection is not characteristic. Disease runs in the background of normal or subfebrile body temperature. The duration of the process is no more than 5-7 days.
Chronic giardiasis observed mainly in children of preschool age and is recurrent in nature.
For chronic diseases are most common symptoms:
General weakness, fatigue, irritability, loss of appetite, headaches, dizziness, poor sleep, the appearance of ticks and hyperkinesis (in the form of bad habits).
Change skin:
pallor, especially the skin (normal numbers of hemoglobin) and nose (marble white skin of the nose);
uneven coloration of the skin in combination with its subikterichnostyu, brownish-colored skin ikterichnoy neck, the lateral surfaces of the abdomen, axillary folds;
follicular keratosis point, dry skin, creating the impression of a so-called goose skin preferentially localized on extensor surfaces of hands and feet, the sides of the abdomen;
discoloration and dryness of palms;
lesion rim lip (from mild dryness to heylita);
atopic dermatitis.
Resistant coated tongue.
Bloating, flatulence, rumbling in the gut, neustoychivyystul with alternating diarrhea and constipation.
Abdominal tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant and above the navel, at the points of the projection of the gallbladder.
Enlargement of the liver.
Intestinal dysbiosis.
In general, the analysis of blood in young children have leukocytosis, eosinophilia, monocytosis, anemia, and older children - leukocytosis, eosinopenia, monotsitopeniya, less SOE.V depending on the predominance of certain symptoms identify the following clinical forms of disease: intestinal, hepatobiliary , asthenoneurotic, toxic-allergic, anemic ismeshannuyu.
Intestinal form of a marked diarrhea and abdominal symptoms. This is an unstable chair, alternating constipation and diarrhea, steatorrhea, malabsorption, mild abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, weight loss, retarded physical development.
For hepatobiliary form Giardiasis is characterized by dyskinesia zhelchevyvodyaschihputey with spasm or atony sphincter, cholestasis. Often failure is combined with biliary gastritis gastroduodenitis pancreatitis.
When asthenoneurotic form giardiasis symptoms of gastro-intestinal tract expressed moderately or weakly. At the forefront are the headaches, irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbance, neurocirculatory dystonia.
Toxico-allergic form of the disease is characterized by more frequent ostrymiallergicheskimi states (urticaria, angioedema). During the acute allergies when Giardiasis stubborn, lingering. It is difficult to drug therapy. Often there is a development of atopic dermatitis, which has a continuously relapsing course. Some patients may damage the joints.
The most accessible method for laboratory diagnosis of giardiasis in children is a scatological study. However, it should be noted that the cysts of Giardia in the stool can not always detect. To improve the efficiency of the method should:
for a fence to use liquid fraction of faeces from the last portion collected from 5-7 seats;
preservation within a few days of portions of liquid feces in a glass container with 10% formalin solution or polyvinyl alcohol;
paint smear feces Lugol's iodine solution or trihromogen toksilina-iron;
In addition to feces is desirable to conduct a study of duodenal contents (portions A and B). For the serological diagnosis of giardiasis using ELISA method. Spetsificheskieantitela found in the blood 2-4 weeks after infection. It should be borne in mind that protivolyamblioznye antibodies can be detected in blood as early as 4-6 weeks after recovery.
In appointing the treatment of giardiasis in children should consider the following factors:
the severity and duration of clinical symptoms of giardiasis;
the presence of background and associated diseases;
efficiency anti lamblic therapy, which was held earlier;
possible source of infection (family members, children's teams). Starting with the treatment of chronic giardiasis of antiparasitic drugs is impractical because it can lead to severe reactions damage the appearance of toxic-allergic complications and exacerbation of clinical symptoms. Therefore, treatment in such cases should be conducted in 3 phases:
Stage I - the elimination of endotoxemia, mechanical removal of Giardia, the improvement of the enzymatic activity of the intestine, correction of immunological protection. Depending on the severity of symptoms of stage I is carried out for 1-2 weeks and includes:
diet, which is aimed at creating conditions that can impair reproduction lamblia (cereals, fruits, vegetables, vegetable oils); limit carbohydrate intake;
reception choleretic drugs, with the advantage goes to holekinetikam and holespazmolitikam;
appointment Enterosorbents (silicate, aluminosilicate, organomineraly);
fermentoterapiyu (results coprogram);
antihistamines.
Stage II - antiparasitic therapy.
Stage III - increase the body's defenses and create conditions that inhibit reproduction of Giardia in the intestine and gallbladder. For this purpose appointed a diet that improves intestinal peristalsis (cereal porridge, vegetable and fruit purees, baked apples, fresh fruit and vegetables, dairy products). In order to create an environment conducive to the destruction of cysts of Giardia, we recommend a decoction of birch buds for 2-3 weeks, and after 2-week break - acceptance of broth bearberry seeds for another 2 weeks.
For correction of the immune response are appointed plant adaptogens (echinacea, Siberian ginseng, etc.), multivitamin complexes. For the elimination of intestinal dysbiosis, fermentopathy prescribe probiotics, prebiotics, enzymes. The third stage takes about 2-3 weeks.
To prevent giardiasis should:
drink only filtered tap water or boiled water;
conducted in closed-organized children's kollektivahobsledovanie children and staff, 2 times a year, and in identifying those that produce cysts of Giardia, sanitize all family members.
Literature
1. Giardiasis in children. Guidelines (NI Zryachkin, S. Central Committee, T. Grozdova et al.), Saratov, 2002, 24s.
2. Mamchur VI, Suremenko NS, Kraus, VA Causal pharmacotherapy protozoal infections and worm infestations. Kiev - Saint - Petersburg, 1997, 123.
3. Addis DG, Juranek DD, Spencer HC Treatment of chealdren with asymptomatic and non diarrheal Giardia infection. Pediatr.Infect. Dis., 1991, N 10, p. 843-846.
4. Davies EG, Elliman DA, Hart CA Manual ChildhoodInfection. Edinburg: Saunders, 2001, 514 p.
5. Long SS, Pickering LK, Prober CG Pediatric infectious diseases. NY, London, Madrid, Melbourne, San Francisco, Tokyo: Churchill Livingstone, 1997, 1713 p.
